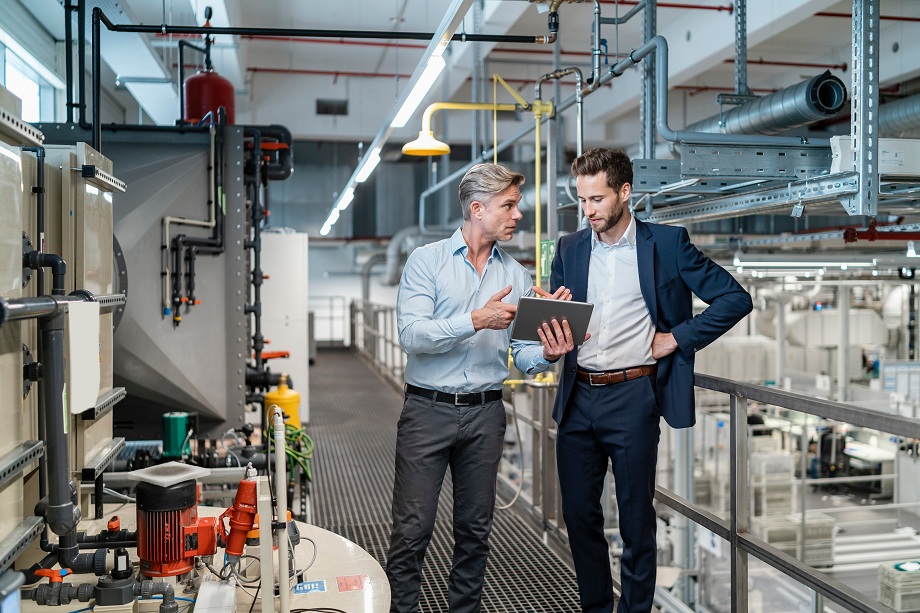
Plant operators ensure their facilities meet the established performance standards and customer service expectations. If you are interested in obtaining a plant operator job, you should be familiar with its general duties. The essential duties for managing all types of plants from power to water are similar. Some responsibilities vary depending on the specific industry you work in. Contact ITI Technical College today for more information.
Types Of Plants That Make Up Our Infrastructure
We are blessed to have a variety of plants that provide the products and services we need. They give us conveniences and luxuries compared to some other less-developed countries. The plants that provide basic services that meet our national lifestyles include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each of these facilities needs competent plant operators to provide these products and services that meet standards of quality and safety.
Plant Operator Duties: Oversee Plant Operations
Plant operators oversee all plant operations from start to finish and delegate some areas of responsibilities to others as needed. They must understand the nature of all operations whether simple or complex including associated equipment and devices. Operators also:
- Oversee any repairs needed and troubleshoot operations
- Work in human resources such as acquiring and training employees
- Oversee general maintenance of the plant
- Adhere to safety and regulatory practices and policies
- Solve problems as they arise
Plant operators must have a standardized plan to cover all essential operations and emergencies that could occur.
| “Plant operators ensure their facilities meet the established performance standards and customer service expectations.” |
Repairs And Troubleshooting
 Equipment, machinery, and electronic devices sometimes malfunction and must be repaired or replaced. Troubleshooting is the way to determine the root cause of why malfunctions occur. Plant operators are trained to understand all systems in their facilities, and this gives them a general idea of where to search for problems that appear.
Equipment, machinery, and electronic devices sometimes malfunction and must be repaired or replaced. Troubleshooting is the way to determine the root cause of why malfunctions occur. Plant operators are trained to understand all systems in their facilities, and this gives them a general idea of where to search for problems that appear.
Plant operators must know where to order parts or equipment that must be replaced and how to change out the old parts or equipment. If it is less expensive to repair things, they must find someone trained to perform the repair. Establishing a general maintenance plan helps lessen the need for repairs and replacements.
Plant Operator Duties: Human Resources
Managers must know how to find and train the best employees. They understand human resource principles and work with other managers or technicians to:
- Create a job duty list for each position in the plant
- Understand how all jobs relate to each other
- Create effective job postings for media
- Orient and train new workers effectively
- Explain employee benefits to employers
Plant operators or assistants must explain safety rules and procedures to protect workers while on the job. They must also explain any labor relations or connections with labor unions.
General Maintenance
A sound general maintenance plan helps reduce the need for and frequency of occurrence of equipment or system breakdowns. It should include the following:
- A complete list of everything that needs regular inspection
- A checklist for showing each item was found to function correctly
- A checklist to mark any issues that need attention
- A plan with dates for inspecting and maintaining all equipment and processes
- Who to report any issues to or who should provide a second opinion
- What to do if a problem arises
All maintenance plans should be updated as necessary to keep operations running smoothly.
Plant Operator Duties: Safety Adherence
 Plant operators must adhere to safety policies and practices to ensure workers are not harmed. Unfortunately, accidents, injuries, and occasional deaths do occur in plants for a variety of reasons. Employees must be trained to follow all safety rules and a list of them must be available to everyone that works in the plant.
Plant operators must adhere to safety policies and practices to ensure workers are not harmed. Unfortunately, accidents, injuries, and occasional deaths do occur in plants for a variety of reasons. Employees must be trained to follow all safety rules and a list of them must be available to everyone that works in the plant.
Federal and state agencies dictate safety rules for all industrial plants. Plant managers participate in training classes to learn to put safety practices into use. Following them is essential to prevent accidents and attract new employees.
Solve Problems Effectively
Managers develop the ability to isolate and solve problems at their core. A simple approach is applying these reasoning skills:
- Identify the problem by using knowledge of the plant, past experiences, and basic components to narrow down the search
- Analyze the problem by considering its underlying factors and root cause
- Use strategies and tools like the 5 Whys, fishbone diagram, or Pareto charts to break down the problems into smaller components
- Solve the problem by using a standard operating procedure or your own experience
- Check your actions to see if they had the desired effect
- If the problem is not solved, go through all the steps again with a team
Associate degree programs provide training for plant and assistant plant operators. Request more information about them and arrange for an initial on-campus visit.
For more information about graduation rates, the median debt of students who completed the program, and other important information, please visit our website: https://iticollege.edu/disclosures/